
NucleicAcidsRes.:首次全面绘制RNA修饰谱揭示癌症热点
来源:生物谷2012-02-2620:29
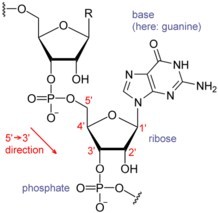 RNA的化学结构,图片来自维基共享资源。
RNA的化学结构,图片来自维基共享资源。
一种新技术有助于研究人员找出促进癌症发生的基因信息的精确位置。
相对于DNA而言,人们对RNA知之较少。澳大利亚国立大学约翰-卡廷医学研究学院ThomasPreiss教授领导的一个研究小组使用一种新的绘图技术来揭示RNA中修饰标记所在的位置。
Preiss教授说,“RNA作为一种信使携带基因信息到细胞内蛋白制造的地方。细胞内的酶能够修饰RNA,同时留下已知为m5C位点的标记。”
“修饰RNA的一些酶经证实与癌症和干细胞生物特征相关联。理解这些修饰的模式将有助于癌症研究人员将他们的关注点集中于RNA在促进癌症产生中所起的作用。”
在这项研究中,研究人员首次在RNA上全面地描绘这些修饰,并鉴定出上万个新的修饰位点。他们发现这些位点要比人们之前所认为的更加普遍,而且不是随机分布的而是有规则分布在遗传标记(geneticlandmark)附近。
这项研究发表在NucleicAcidsResearch期刊上。(生物谷:towersimper编译)
doi:10.1093/nar/gks144PMC:PMID:
Widespreadoccurrenceof5-methylcytosineinhumancodingandnon-codingRNA
JeffreyE.Squires,HardipR.Patel,MarcoNousch,TennilleSibbritt,DavidT.Humphreys,BrianJ.Parker,CatherineM.SuterandThomasPreiss
Themodifiedbase5-methylcytosine(m5C)iswellstudiedinDNA,butinvestigationsofitsprevalenceincellularRNAhavebeenlargelyconfinedtotRNAandrRNA.Inanimals,thetwom5CmethyltransferasesNSUN2andTRDMT1areknowntomodifyspecifictRNAsandhaverolesinthecontrolofcellgrowthanddifferentiation.Tomapmodifiedcytosinesitesacrossahumantranscriptome,wecoupledbisulfiteconversionofcellularRNAwithnext-generationsequencing.Weconfirmed21ofthe28previouslyknownm5CsitesinhumantRNAsandidentified234noveltRNAcandidatesites,mostlyinanticipatedstructuralpositions.Surprisingly,wediscovered10275sitesinmRNAsandothernon-codingRNAs.WeobservedthatdistributionofmodifiedcytosinesbetweenRNAtypeswasnotrandom;withinmRNAstheywereenrichedintheuntranslatedregionsandnearArgonautebindingregions.WealsoidentifiedfivenewsitesmodifiedbyNSUN2,broadeningitsknownsubstraterangetoanothertRNA,theRPPH1subunitofRNasePandtwomRNAs.Ourdatademonstratesthewidespreadpresenceofmodifiedcytosinesthroughoutcodingandnon-codingsequencesinatranscriptome,suggestingabroaderroleofthismodificationinthepost-transcriptionalcontrolofcellularRNAfunction.







